Range Rover L460 – Configurable Drivers Assist (MY24 Only): Mastering CCF with JLR Engineering Tools
For technicians specializing in the latest Range Rover L460 (Model Year 2024), the ability to accurately modify the Car Configuration File (CCF) is paramount, especially concerning the sophisticated Configurable Drivers Assist systems. The JLR Engineering Tool (JET) environment, accessed via specialized interfaces and software, enables deep-level CCF editing – a critical skill for activating latent features, resolving misconfigurations, or performing OEM-compliant retrofits. A common challenge encountered in workshops is the “Feature Not Available” message despite hardware presence, often directly attributable to incorrect or incomplete CCF coding. Precise manipulation of these parameters using tools like the SX-Tool and DOIP VCI within the TOPIx ecosystem is the definitive solution.
Technical Deep Dive: Configuring MY24 Drivers Assist Systems
Core Concepts & Technologies
Understanding the interplay of these technologies is essential for successful configuration:
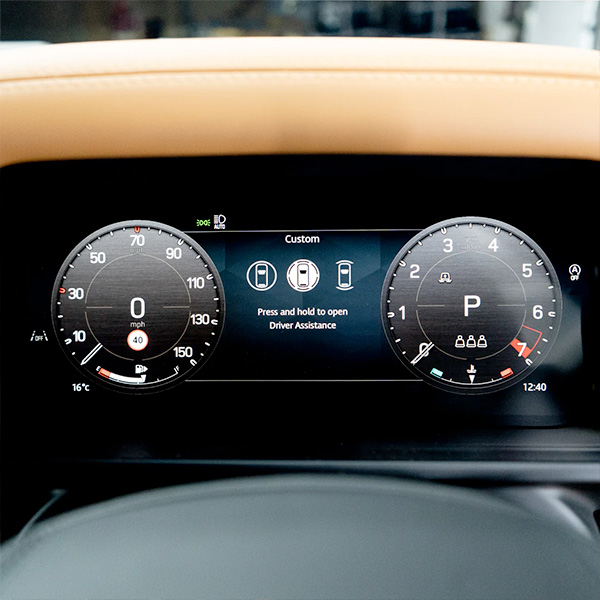
- Drivers Assist: Refers to the suite of MY24 L460 Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) like Adaptive Cruise with Stop & Go, Lane Keep Assist, Blind Spot Assist, Rear Cross Traffic Alert, and 3D Surround Camera functionality. Many features require explicit activation and configuration within the vehicle's CCF.
- JLR Coding: The process of modifying vehicle software parameters, primarily the CCF, using specialized JLR-approved or compatible engineering tools. This goes beyond basic diagnostics to enable/disable features and set configuration flags.
- CCF (Car Configuration File): The central electronic “build sheet” stored on the L460's Central Configuration Module (CCM). It defines every enabled feature, option, and parameter based on the vehicle's original specification (VO) and subsequent coding changes. Incorrect CCF settings are the primary cause of Drivers Assist malfunctions or unavailable features post-hardware installation.
- SX-Tool (JLR Engineering Software): A third-party engineering tool providing a user interface for reading, editing, and writing the CCF and performing other advanced coding functions on JLR vehicles. It interfaces with the vehicle via a DOIP VCI.
- TOPIx (JLR Cloud Diagnostics): JLR's official cloud-based diagnostic and programming platform. While Pathfinder is used for standard diagnostics and programming, engineering-level CCF work often requires supplementary tools like SX-Tool for direct editing. TOPIx provides essential context like the original Vehicle Order (VO).
- DOIP VCI (Diagnostics over Internet Protocol Vehicle Communication Interface): The mandatory hardware interface adhering to the DOIP standard (ISO 13400) required for communicating with the MY24 L460's high-speed Ethernet network. A JLR-compatible, stable, and capable DOIP VCI is non-negotiable for reliable CCF access and coding.
Hypothetical CCF Activation Process for Drivers Assist Feature
Disclaimer: This is a generalized process outline. Always refer to official procedures and vehicle-specific data.
- Preparation: Connect a stable battery maintainer/power supply (>80A). Ensure the workshop environment has stable internet for TOPIx. Power on the vehicle (Ignition Mode 6 / Engine Running if required by procedure).
- Vehicle Identification & Backup: Using your DOIP VCI connected to the L460's OBD port and Ethernet network, launch SX-Tool. Read the VIN and current CCF from the Central Configuration Module (CCM). Perform a full, verified backup of the original CCF – this is critical for recovery.
- Feature Identification & VO Check: Consult TOPIx using the VIN to confirm the original Vehicle Order (VO) and build spec. Identify the specific CCF parameters (AS-BUILT data lines or feature flags) related to the target Drivers Assist feature (e.g., “Blind Spot Assist Active”).
- CCF Editing: Within SX-Tool, locate the identified CCF parameters. Modify the values according to the target configuration (e.g., changing “BLIS_ACTIVE” from '00' to '01'). Validate syntax and logical consistency of changes.
- CCF Writing & Verification: Write the modified CCF back to the vehicle's CCM using SX-Tool via the DOIP VCI. This process is time-sensitive and power-critical. Upon successful write, perform a complete vehicle sleep cycle (Key Off, lock vehicle, wait 15+ minutes).
- Module Reset & Calibration: Wake the vehicle. Use TOPIx/Pathfinder to perform necessary module resets (e.g., CCM reset, Head Unit reboot). Some Drivers Assist features (like Lane Keep) will require sensor recalibration using Pathfinder and appropriate targets.
- Functional Test: Thoroughly road-test the vehicle to verify the activated feature functions correctly and that no DTCs related to the configuration are present.
Essential Tools & Setup
- DOIP VCI Interface: A high-quality, JLR-compatible DOIP interface (e.g., MongoosePro JLR, OE-level JLR VCI, or verified equivalents) is mandatory. USB passthrough devices are insufficient.
- Stable High-Current Power Supply: A >80A battery maintainer is essential to prevent voltage drop during CCF writing, which can brick modules.
- Engineering Software: SX-Tool JLR Engineering Software or equivalent capable of reading/writing CCF and performing necessary security access.
- JLR Official Diagnostics: Subscription to TOPIx with Pathfinder for VIN-specific data, module programming, resets, and calibration procedures.
- Technical Information: Access to reliable CCF parameter databases and wiring diagrams (e.g., via TOPIx Workshop Manuals).
Common Challenges & Mitigation Strategies
- “Configuration Incompatible” Errors: Caused by incorrect parameter changes or conflicts. Solution: Meticulously verify changes against known-good data or VO. Restore backup and re-attempt.
- CCF Write Failures/Module Bricking: Primarily due to voltage drop or unstable VCI connection. Solution: Rigorous adherence to power supply requirements and using a proven DOIP VCI. Always backup first!
- Feature Activation But Non-Function: Often due to missing calibration, incorrect dependency settings, or incompatible hardware. Solution: Verify all required sensors/modules are present and functional via diagnostics. Perform mandatory calibrations using TOPIx. Check all prerequisite features are enabled in CCF.
- Security Access Denied: SX-Tool or the VCI fails to gain security access. Solution: Ensure software/VCI firmware is up-to-date. Verify correct procedure execution (e.g., ignition state). Try alternative security algorithms if supported.
- Network Communication Issues: DOIP communication failures. Solution: Check Ethernet cable integrity, VCI drivers, firewall settings blocking communication, and vehicle network gateway status.
Essential Device: The SX-Tool for JLR Engineering
For reliable and efficient JLR coding and CCF manipulation on the MY24 L460, the SX-Tool is a cornerstone tool. It provides the necessary interface and functionality to:
- Read and Decrypt the CCF from the CCM.
- Edit CCF parameters directly in a structured format.
- Perform Security Access (e.g., to the CCM).
- Write the modified CCF back to the vehicle.
- Interface seamlessly with capable DOIP VCI devices.
Acquire the Industry-Standard Tool: For technicians serious about MY24 L460 Drivers Assist configuration and advanced JLR diagnostics, the official SX-Tool JLR Engineering Software is indispensable. Ensure you source it from reputable providers for guaranteed functionality and support.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Can I use a generic OBD2 scanner for L460 Drivers Assist CCF coding?
No. Generic OBD2 scanners lack the capability to access the Central Configuration Module (CCM) via DOIP or perform the security access and deep CCF read/write operations required. A specialized DOIP VCI and engineering software like SX-Tool are mandatory.
Why is TOPIx needed if I'm using SX-Tool for CCF editing?
TOPIx provides the critical Vehicle Order (VO) – the vehicle's original build specification. This is essential for verifying which features are *supposed* to be active and for identifying the correct CCF parameters to change. It's also required for module resets and calibrations post-CCF modification.
What happens if the CCF write is interrupted (e.g., power loss)?
This is a critical failure scenario. An interrupted CCF write can corrupt the Central Configuration Module (CCM), potentially rendering the vehicle inoperable (“bricked”) and requiring a new CCM module and potentially complex restoration via JLR coding with dealer-level tools. This underscores the absolute necessity of a stable, high-current power supply (>80A) during the write process.
Is it possible to enable features not included in the original Vehicle Order (VO)?
Technically, CCF editing with SX-Tool can change flags. However, enabling features requires compatible hardware (sensors, modules, wiring) and potentially additional software configuration/licensing. Enabling features outside the original VO is an OEM retrofit and requires extensive expertise, correct parts, and carries risks of system instability or warranty implications. Proceed with extreme caution and thorough research.
My Drivers Assist features stopped working after a software update. Can CCF coding fix this?
Possibly. Software updates occasionally reset modules or introduce configuration mismatches. Using SX-Tool to read the CCF and compare it against the known correct configuration (based on VO and hardware) can identify if parameters were inadvertently changed. Correcting these via CCF editing is often the solution, after ruling out sensor faults or calibration needs via TOPIx diagnostics.
Conclusion: Precision Engineering for Advanced ADAS
Configuring the Drivers Assist suite on the MY24 Range Rover L460 demands a precise understanding of the Car Configuration File (CCF) and mastery of specialized tools. The interplay of JLR coding practices, the SX-Tool for direct CCF manipulation, TOPIx for diagnostics and calibration, and a robust DOIP VCI forms the essential toolkit. Success hinges on meticulous process adherence, unwavering attention to power stability, comprehensive backups, and rigorous post-coding validation. Overcoming challenges like CCF write failures or feature misconfiguration requires both technical knowledge and reliance on proven, high-quality equipment.
Master the MY24 L460: For technicians and workshops committed to excellence in Drivers Assist configuration, advanced diagnostics, and OEM-compliant retrofits, investing in the right tools and expertise is non-negotiable. Explore the capabilities of the SX-Tool JLR Engineering Software and find comprehensive support solutions at jlrcoding.com – your partner in complex JLR programming and retrofit tasks.
Meta Description: Expert guide to configuring MY24 Range Rover L460 Drivers Assist using JLR coding, CCF editing, SX-Tool, TOPIx & DOIP VCI. Solve activation issues & learn best practices.
Keywords: Drivers Assist, jlr coding, CCF, sx-tool, topix, doip vci, Range Rover L460 ADAS, JLR CCF editing, Land Rover programming, SX-Tool JLR, JLR engineering tool, Central Configuration Module, MY24 Range Rover coding.
Long Tail Keywords: “how to activate blind spot assist range rover l460 my24”, “sx-tool configuration for range rover drivers assist”, “fix drivers assist not available range rover l460 ccf”, “doip vci requirements jlr coding”, “topix vs sx-tool for land rover configuration”.
Tags: Range Rover L460, MY24, Drivers Assist, ADAS, JLR, Land Rover, CCF, Car Configuration File, Coding, Programming, SX-Tool, TOPIx, DOIP, VCI, JLR Engineering, Diagnostics, Retrofit, Advanced Driver Assistance Systems, Central Configuration Module, Technical Guide.